Papermaking wastewater and its characteristics
Papermaking wastewater
Papermaking wastewater includes wastewater produced by two processes in the paper industry for pulping and papermaking. The water volume is large with high color, a large amount of suspended matter, high concentration of organic matter and complex components.
General papermaking wastewater is divided into:
(1) The sewage discharged from the beater and the refiner, called beating sewage.
(2) Paper machine sewage, which can be used directly as white water.
(3) The waste liquid produced by cooking wood pulp (or grass pulp), also known as black liquor.
The features of papermaking wastewater
(1) Difficult biodegradable organic matter is mainly derived from lignin and macromolecular carbohydrates contained in fiber raw materials.
(2) Chroma. The residual lignin contained in the pulping wastewater is highly colored.
(3) Easy biodegradable organic matter includes low molecular weight hemicellulose, methanol, acetic acid, formic acid, sugar, and etc.
(4) Toxic substances. Rosin acids and unsaturated fatty acids are contained in black liquor.
(5) Suspended matter includes settleable suspended solids and non-settable suspended solids, mainly fiber and fiber fines (ie broken fiber fragments and hybrid cells)
(6) Acid-base poisons. The pH value of alkaline pulping wastewater is 9~10; the pH value of acid pulping wastewater is 1.2~2.0.
National Service Hotline:400-608-6866 Online
Conventional processes and limitations
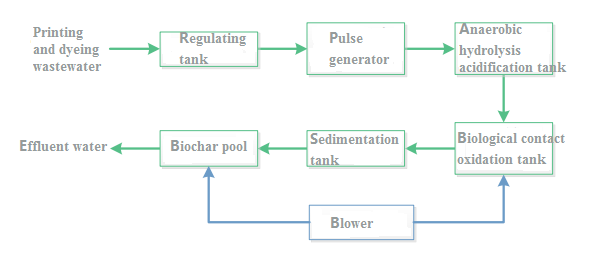
Hydrolysis Acidification-Biological Contact Oxidation- Process for Printing and Dyeing Wastewater with biochar
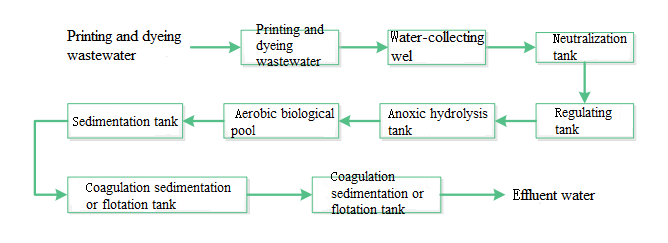
Combined process for printing and dyeing wastewater
The limitations of conventional processes
1. High requirements of operating conditions
2. Large energy consumption and high operating cost
Package product
Applications